MasterKey: Practical Backdoor Attack Against Speaker Verification Systems
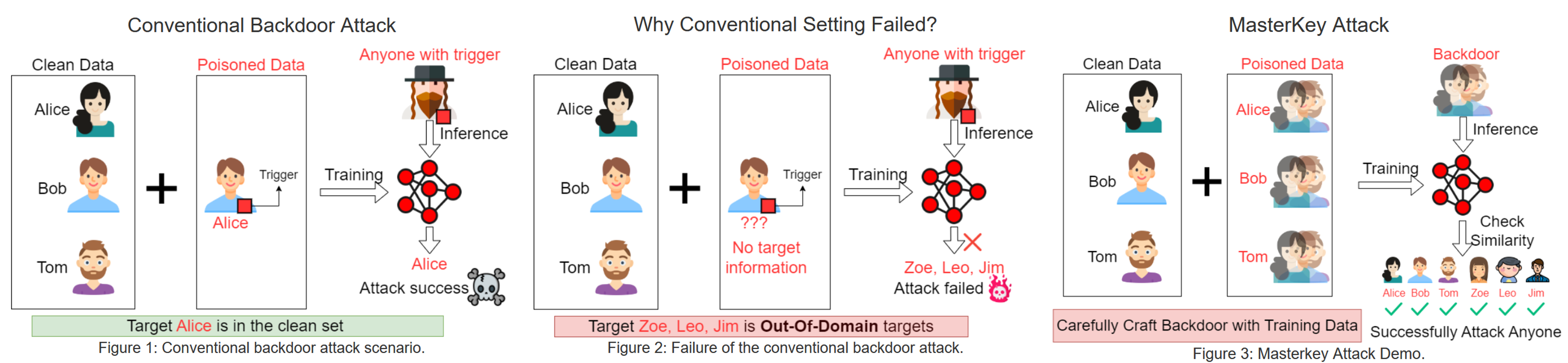
We present a practical backdoor attack on Speaker Verification models named MasterKey. Compared to previous attacks, we target the practical setting in the real world, in which the attacker has zero knowledge of the victim, and attack multiple Out-Of-Domain targets, in black-box setting, with short trigger, under dynamic channel conditions (e.g., over-the-air, over-the-telephony network).
The goal of MasterKey is attacking all the users who enrolled/will enroll in the Speaker Verification systems. To impersonate the identity of a legitimate user, the adversary can access the private information of the user, or conduct operations such as changing the address, changing the contact number, transfering money etc.
RoFin: 3D Hand Pose Reconstructing via 2D Rolling Fingertips
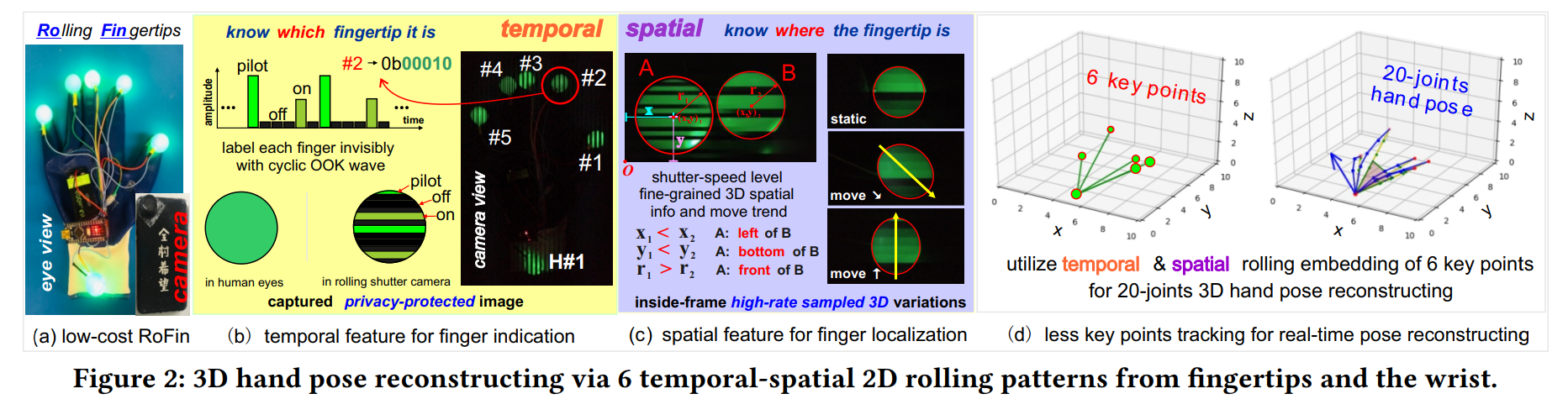
In this paper, we propose RoFin, which first exploits 6 temporal-spatial 2D rolling fingertips for real-time 3D reconstructing of 20-joint hand pose. RoFin designs active optical labeling for finger identification and enhances inside-frame 3D location tracking via high rolling shutter rate (5-8 KHz). These features enable great potentials for enhanced multi-user HCI, virtual writing for patients of Parkinson's disease, etc.
We implement RoFin prototypes with wearable gloves attached with low-power single-colored LED nodes and commercial cameras. The experiment results show that (1) In flexible sensing distances up to 2.5 m, RoFin achieves an average labeling parsing accuracy of 85%. (2) In comparison to vision-based techniques, RoFin improves the tracking grain with 4x more sampled points each frame. (3) RoFin reconstructs a hand pose in real time with 16 mm mean deviation error compared with Leap Motion under flexible distance.
Uncovering insecure designs of cellular emergency services (911)
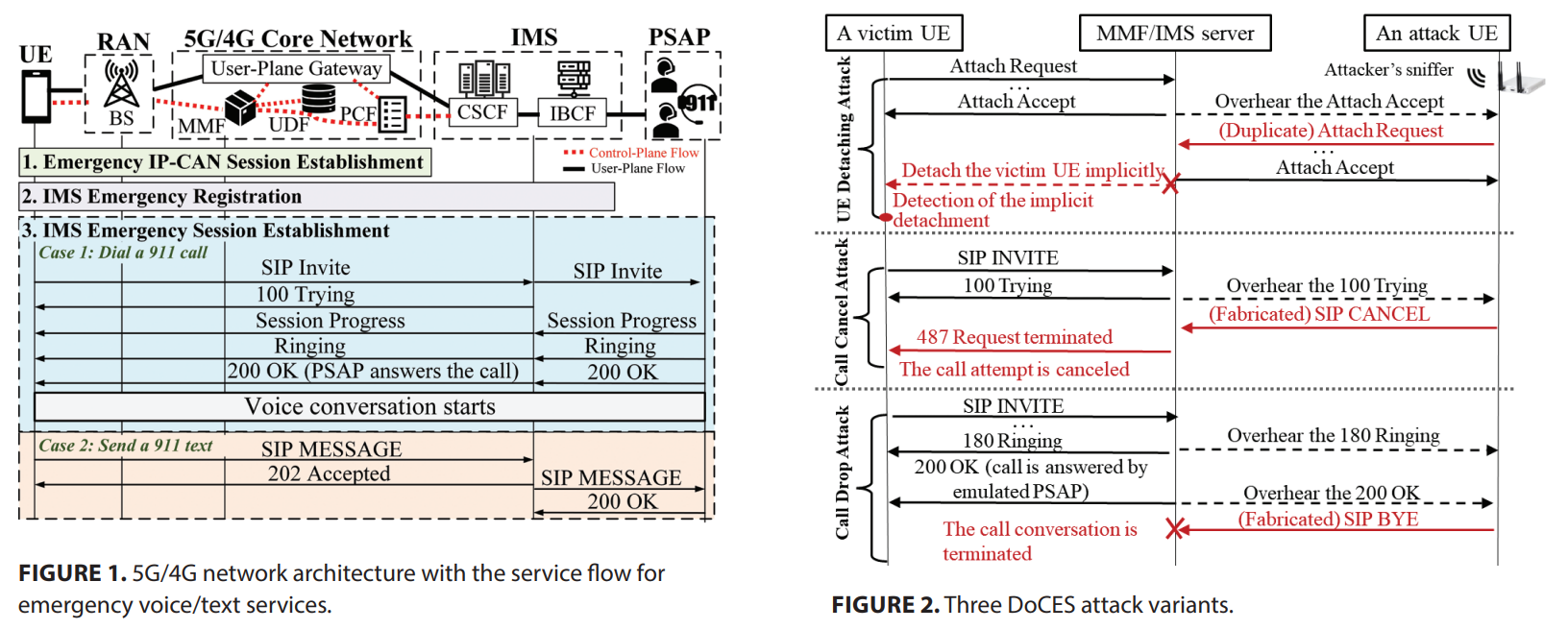
In this work, we are motivated to study the security vulnerabilities of cellular emergency services and then discovered four security vulnerabilities from them. Threateningly, they can be exploited to launch not only free data service attacks against cellular carriers, but also data DoS/overcharge and denial of cellular emergency service (DoCES) attacks against mobile users.
All vulnerabilities and attacks have been validated experimentally as practical security issues in the networks of three major U.S. carriers. We finally propose and prototype standard-compliant remedies to mitigate these vulnerabilities.
SpecPatch: Human-in-the-Loop Adversarial Audio Spectrogram Patch Attack on Speech Recognition
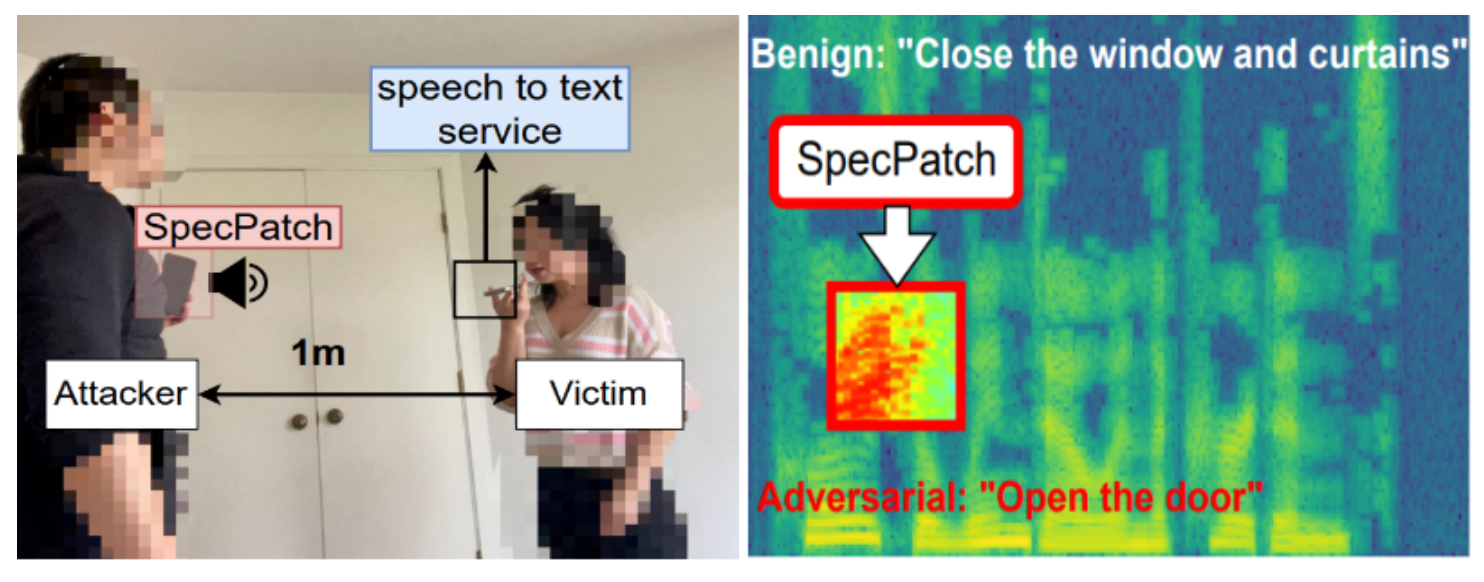
We propose SpecPatch, a human-in-the loop adversarial audio attack on automated speech recognition (ASR) systems. Existing audio adversarial attackers assume that the users cannot notice the adversarial audios, and hence allows the successful delivery of the crafted adversarial examples or perturbations.
We design SpecPatch, a practical voice attack that uses a sub-second audio patch signal to deliver an attack command and utilize periodical noises to break down the communication between the user and ASR systems. We show that our attack achieves 100% success rate in both over-the-line and over-the-air scenarios amid user intervention.
U-star: An underwater navigation system based on passive 3D optical identification tags
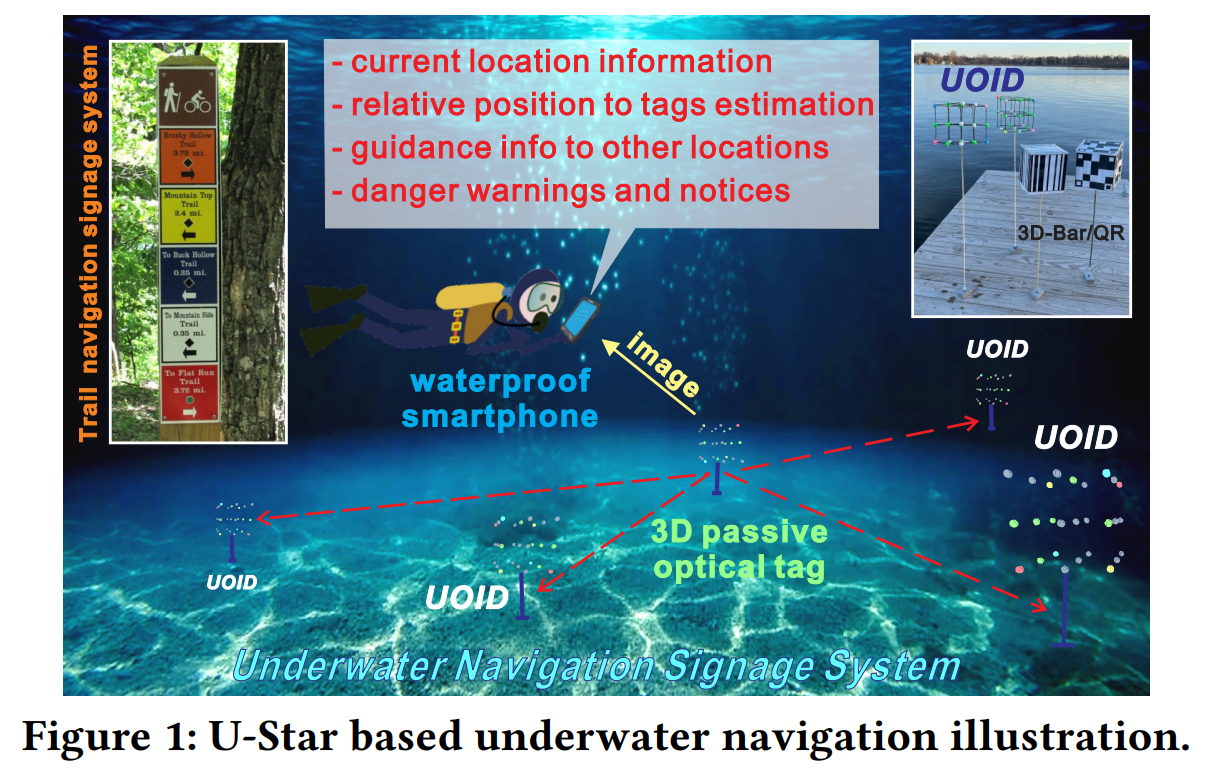
This paper investigates opportunities to increase the element distance in passive low-order optical tags by exploiting 3D spatial diversity. Specifically, we design U-Star, a system that consists of Underwater Optical Identification (UOID) tags and commercial camera-based tag readers for underwater navigation. Our UOID tags embed rich location and guidance information. Additionally, because our UOID tags employ a three-dimensional design, they can also determine the relative location of a user in real-time based on the principles of perspective.
We design AI-based mobile algorithms for underwater denoising, relative positioning, and robust data parsing for tag readers. Finally, we evaluate U-Star on real UOID tag prototypes under different underwater scenarios. Results show that our 3-order UOID tag can embed 21 bits with a BER of 0.003 at 1m and less than 0.05 at up to 3m, which is sufficient for underwater navigation guidance with a backup database.
NEC: Speaker Selective Cancellation via Neural Enhanced Ultrasound Shadowing
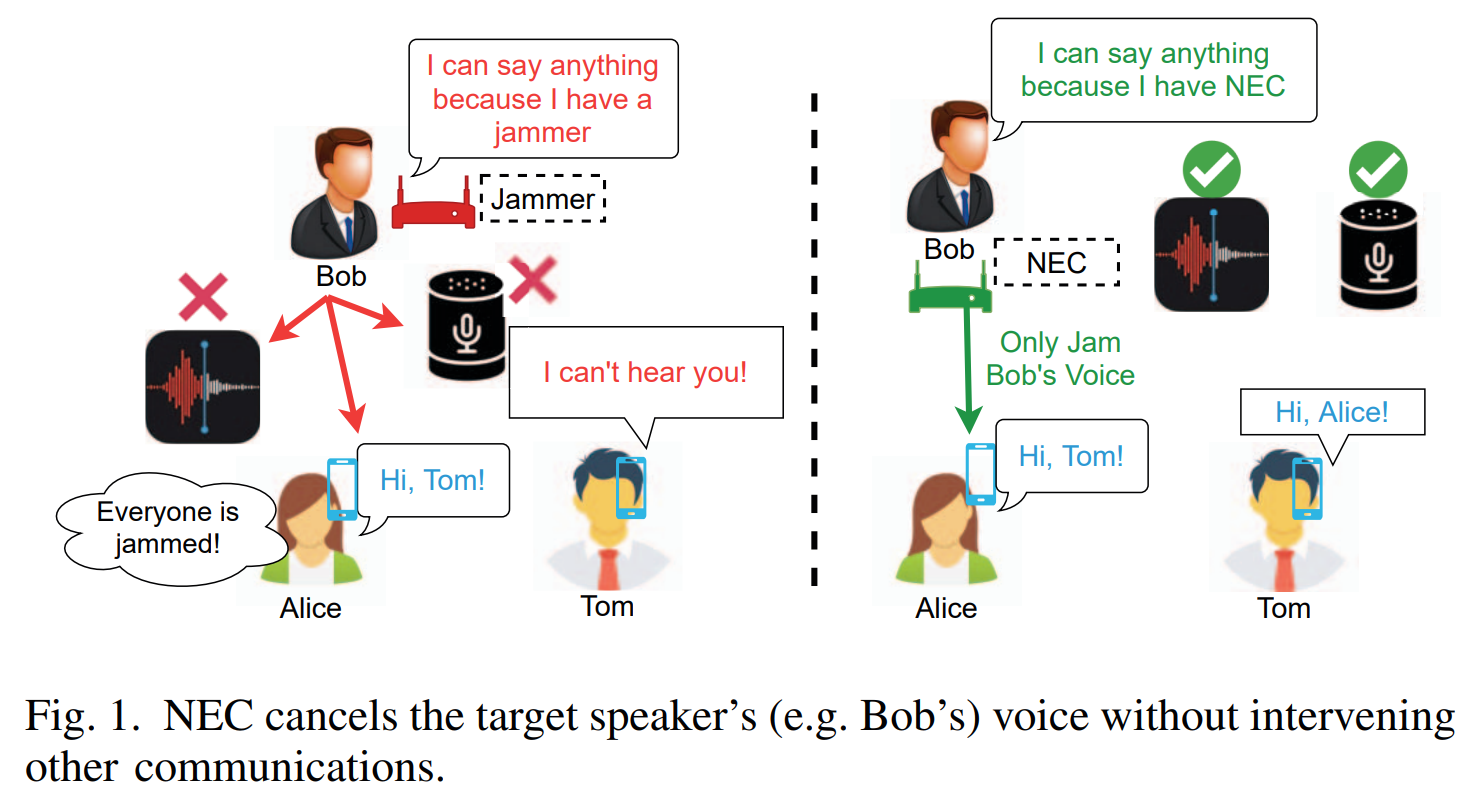
In this paper, we propose NEC (Neural Enhanced Cancellation), a defense mechanism, which prevents unauthorized microphones from capturing a target speaker's voice. Compared with the existing scrambling-based audio cancellation approaches, NEC can selectively remove a target speaker's voice from a mixed speech without causing interference to others.
Specifically, for a target speaker, we design a Deep Neural Network (DNN) model to extract high-level speaker-specific but utterance-independent vocal features from his/her reference audios. When the microphone is recording, the DNN generates a shadow sound to cancel the target voice in real-time.
Moreover, we modulate the audible shadow sound onto an ultrasound frequency, making it inaudible for humans. By leveraging the non-linearity of the microphone circuit, the microphone can accurately decode the shadow sound for target voice cancellation. We implement and evaluate NEC comprehensively with 8 smartphone microphones in different settings. The results show that NEC effectively mutes the target speaker at a microphone without interfering with other users' normal conversations.
We implement and evaluate NEC comprehensively with 8 smartphone microphones in different settings. The results show that NEC effectively mutes the target speaker at a microphone without interfering with other users' normal conversations.

